IP
Address
This is one of the crucial services on the Internet, greatly facilitating the
access of users to websites, by helping each visitor refer to the desired websiteonly by typing its alpha-numeric
name (domain name) in the browser instead
of its real numeric system name (IP address).
001011100011000100101110001100100011010100110000
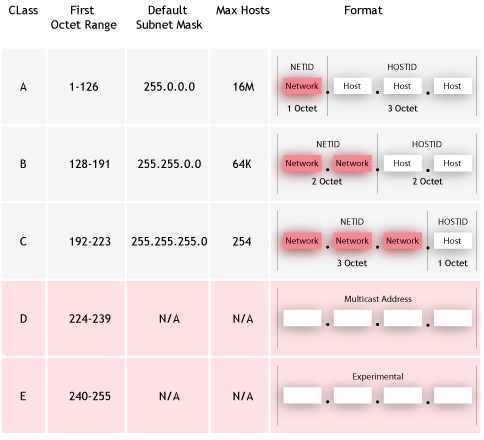
Class
A IP addresses
Net
Host
123.
23.41.88
Net
Host
133.23. 41.88
Net
Host
196.23.41. 88
www.ntchosting.com has address 216.65.1.250
host 216.65.1.250
250.1.65.216.in-addr.arpa domain name pointer www.ntchosting.com.
This is one of the crucial services on the Internet, greatly facilitating the access of users to websites, by helping each visitor refer to the desired websiteonly by typing its alpha-numeric name (domain name) in the browser instead of its real numeric system name (IP address).

001011100011000100101110001100100011010100110000
Net Host
123. 23.41.88
Net Host
133.23. 41.88
Net Host
196.23.41. 88
www.ntchosting.com has address 216.65.1.250
host 216.65.1.250
250.1.65.216.in-addr.arpa domain name pointer www.ntchosting.com.

No comments:
Post a Comment